Arch Pain
Pain in the foot arch is due to tissue inflammation in that region. In addition, factors such as arch structure, foot pronation, overweight, improper footwear, physical activities, and foot types may be related to the development of pain.
The foot comprises three plantar arches: the medial longitudinal, the lateral longitudinal, and the transverse. These, in turn, are made up of various bones and ligaments. These structures are crucial since they support and distribute all the body weight on the feet.
Two muscles are responsible for promoting stability in the foot arches. One is known as intrinsic and is characterized by covering only the foot structures. The function of this tissue is to improve alignment and control the position of the foot arch, which makes it essential for preserving body balance. The other muscle is extrinsic, starting in the leg and extending to the toes, directly influencing ankle function.
CAUSES OF ARCH PAIN
Arch height
Pain mainly occurs in the medial longitudinal arch, as it is responsible for performing essential functions such as absorbing and supporting impacts during walking. The arch is formed during childhood, with anatomical changes that vary from person to person. These are usually hereditary and can lead to the loss of impact absorption and cushioning efficiency.
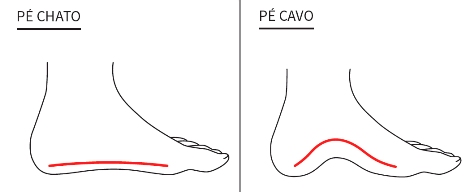
These variations, known as flat foot and high arch, often cause pain in the arch region more quickly than in standard feet. Pain affects flat feet the most because the medial longitudinal arch considerably decreases or even disappears in some cases. The high arch is the opposite: excessive elevation of the medial longitudinal arch.
CAUSES OF ARCH PAIN
Arch height
Pain mainly occurs in the medial longitudinal arch, as it is responsible for performing essential functions such as absorbing and supporting impacts during walking. The arch is formed during childhood, with anatomical changes that vary from person to person. These are usually hereditary and can lead to the loss of impact absorption and cushioning efficiency.
These variations, known as flat foot and high arch, often cause pain in the arch region more quickly than in standard feet. Pain affects flat feet the most because the medial longitudinal arch considerably decreases or even disappears in some cases. The high arch is the opposite: excessive elevation of the medial longitudinal arch.
A flat foot is characterized by a lower arch or even the absence of the arch. The entire sole touches the ground in a flat foot, providing a broad support area. However, the fascia (tissue supporting the longitudinal arch) is stretched in flat feet. Consequently, the cushioning capacity of this foot decreases, overloading the tissue and causing pain in the region.
A pe cavus is represented by a raised and prominent arch, which provides less support to this foot type. Consequently, the bones that form the arch are compressed, increasing joint friction and overloading the ligaments, causing foot pain. In addition, the plantar fascia becomes contracted and tenser, contributing to its inflammation.
Alignment
Foot alignment is correlated to the movement performed by the foot during walking. It can be classified as neutral (aligned), pronated (deviation inward), or supinated (deviation outward). Usually, slight deviations occur while walking to improve foot cushioning. However, excessive misalignment can cause pain.
In supinated foot alignment, body pressure is exerted on the lateral part of the foot because the ankle deviates outward. It is also expected to experience pain because the foot structures undergo profound alterations. In pronated foot alignment, foot function is modified, and pressure is concentrated on the inner sole. The reason for this change is the inward deviation of the ankle, which also compromises cushioning and load distribution in the plantar arch.
Overload and arch pain
The appearance of arch pain is closely related to overload. For example, being overweight is one of the causes because every extra kilogram in a person’s body exerts more pressure on the foot.
A fact that proves this is that 62.3% of men over 100kg have experienced foot pain, according to the study “Brazilian Feet”, conducted between February and March 2012, involving 26,339 people. In the case of women, only 6.9% have never experienced such pain.
Sudden increases in physical activity and excessive training without guidance are also harmful in the case of athletes. In 34% of men and 28% of women, sole pain occurred after continuous intense activity.
MAIN PATHOLOGIES THAT CAUSE ARCH PAIN
Plantar Fasciitis
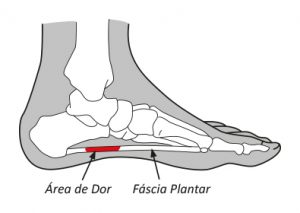
Plantar fasciitis is a well-known pathology. It is considered the leading cause of foot pain and significantly affects the plantar arch. Fasciitis is caused by the plantar fascia inflammation, a connective tissue that begins at the base of the heel and extends throughout the sole. The fascia becomes inflamed when this region is overloaded, causing unwanted pain.
Inflammation can be linked to high arches, flat feet, being overweight, improper footwear, and high-intensity physical activities. People who stand for long periods are more likely to develop fasciitis. Typically, the pain is more acute after long periods of rest because the plantar fascia tends to contract and then be forced again. When stretched throughout the day, the pain may disappear and only return at the end of the day.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Insufficiency (Collapsed Arch)
In cases of inflammation in the posterior tibial tendon, arch pain can occur because the tissue passes through the inner ankle region and runs through the arch to the base of the toes. Initially, the syndrome begins with inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon caused by increased tissue tension. Excessive strain on this tendon can lead to wear and tear and loss of strength in this structure.
This condition is more common in severely pronated feet (as in the image below) due to increased traction on the tibial tendon by stretching the structure. According to the study “Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction“, when inflammation is not promptly treated, it can cause posterior tibial tendon insufficiency, resulting in collapsed arches and possible arch pain.
Bone fractures
Several bones slide against each other in the arch region to cushion the step. Due to its excellent mobility, bone fractures in the arch are less common but can occur in extreme traumatic events. An example is an ankle sprain, which can lead to a navicular bone fracture. When this movement is impaired for some reason, such as bone misalignment or gait error, wear can occur in the area, resulting in a stress fracture.
Navicular fracture: the navicular is the bone at the top of the foot arch, adequately positioned by many ligaments. When a sprain occurs, the ligaments and tendons attached to the bone can be stretched quickly, causing a small bone fraction to be torn away. The symptoms are intense pain after the traumatic event, swelling, and bruising.
Stress fracture: can occur in any bone in the foot. The fracture is generated by an excessive and repetitive overload on the bone tissue, causing it to rupture. The symptoms are pain that worsens with physical activity and improves with rest, which can be accompanied by swelling in the area.
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
The most appropriate procedure for pain relief will depend on the diagnosis. Therefore, in case of acute or persistent pain, it is advisable to seek a specialist to indicate the best treatment. Depending on the diagnosis, imaging tests, temporary physical activity restrictions, and in rare cases, surgery may be necessary. See below for the most frequent treatments:
Biomechanical correction
Gait deviation can be corrected by specific and adequate training that strengthens the foot, ankle, and knee muscles. Lateral elevation insoles that correct misaligned gait are also effective for this type of adjustment. In addition, insoles improve foot cushioning by redistributing pressure on the feet more efficiently, avoiding arch overload.
Manual Therapy
It is the manual manipulation of tissues to generate relaxation and reposition the joint. The movements are a bit firmer but are commonly known as massage and stretching.
Functional Taping
It is a physiotherapy technique that promotes stability and protection without unnecessarily limiting movement. It uses tape (elastic or inelastic) to maintain the ideal positioning of the foot joints.
Acupuncture and Dry Needling
Fine needles are used to reduce pain during the application of this technique. In traditional Chinese acupuncture, the aim is to balance the body’s energies to improve symptoms. On the other hand, dry needling is a procedure that, through the minor injuries caused by the needle, increases metabolism in the plantar fascia and stimulates tissue repair.
Night Splint
A device that keeps the feet in a stretched position while a person is sleeping. It helps to prevent the contraction of the fascia, avoiding discomfort in the foot’s arch at the beginning of the day.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
The use of medication helps control pain and inflammation, but a doctor must prescribe them. Using them helps to relieve symptoms but does not solve the factor that causes complications. Therefore, it is essential to use them in conjunction with other treatments.
Surgery
In extreme cases, surgical procedures may be recommended when repairing injured structures or repositioning the foot arch is necessary. The procedure depends on the reason that is causing the pain in the plantar arch region.
FEET WITHOUT PAIN ® CUSTOM INSOLES AND SHOES FOR ARCH PAIN
Custom insoles and shoes from Feet Without Pain can protect your foot and support the plantar arch removing the overload with each step. The Feet Without Pain insole is custom-made, ensuring you have the ideal support under this region. It significantly reduces the overload deposited in the foot arch when walking, running, or climbing stairs. Custom insoles are a quick and efficient way to address the root cause of the problem.

Feet Without Pain shoes, also custom-made, perfectly accommodate your feet’s dimensions preventing too much pressure on the sides or too much space and consequent lack of support.
In addition, Feet Without Pain offers shoes with 3D printed soles that provide perfect softness and support for your foot arch to have cushioning and protection.
The sole of your shoe shouldn’t be too rigid to prevent it from damaging the foot arch. A shoe with a stiff sole does not allow mobility during walking, much less help absorb the impacts that arrive in the region. It is also recommended that the shoe have a “clearance” of 1.5cm in length to prevent them from tightening the feet while walking.

Regarding footwear, aesthetics are important, but function and comfort should be noticed. That’s why you can choose from 20 different custom-made shoe models Feet Without Pain offers.
Before getting a custom-made insole and shoe, a detailed evaluation is carried out with our specialists to detect the cause of the pain and thus design the insoles and shoes. We also use technological devices such as the baropodometer and 3D scanner to complement the evaluation and improve the quality of our product, made with millimetric digital precision.

The insoles and shoes are made with 3D technology and millimetric digital precision, after a free evaluation of the feet, ankles, and knees, with our specialists. Check out all its benefits now:
- Elimination or reduction of pain;
- Injury prevention;
- Increased comfort;
- Perfect fit;
- More time standing without pain;
- Prevention of pathology progression;
- Improved shock absorption;
- Improved sports performance.
The perfect insole for your foot arch, plus a custom-made shoe, represents a complete solution for those suffering from foot arch pain.
SPORTS
Runners are constantly exposed to various injuries because they strain their legs, feet, and ankles. Left untreated, arch injuries can keep athletes away from the sport for longer than expected.
Marathon runners are more affected during running, mainly when the arch pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. Since this sport requires longer runs, the fascia is significantly strained and worn out, stimulating this tissue’s inflammation.
TIPS AND FACTS ABOUT THE ARCH OF THE FOOT
It is recommended to consult a specialist when a person feels pain in the arch of the foot region. However, some basic advice can help relieve and prevent pain in this area. Here are some of them:
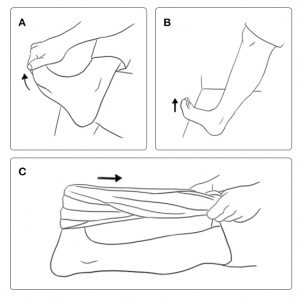
Stretching: stretching the feet and the back of the leg (calf) can be very good for preventing pain in the foot’s arch. The easiest way to stretch these areas is by using your hands to pull your toes back (A). Another way to stretch is to place the tip of your feet on the wall, keeping your heel on the ground and bringing your knee closer to the wall (B). Lastly, you can sit on the floor, lean your entire back against the wall, and keep your legs straight, forming a 90° angle between your legs and trunk. To make the stretch even more challenging, place a towel on your feet tip and pull it towards your body (C).
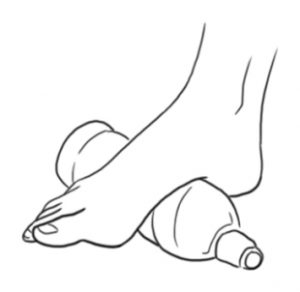
Ice: freeze a water bottle and position your foot on it, fitting it into the arch of your foot. Make small movements back and forth, keeping the bottle in the arch region for 15 to 20 minutes on each foot. This practice is excellent for quick pain relief.
Arch pain exercise stretching
Wearing proper footwear: shoes must be properly fitted for each person’s foot, providing support, comfort, and cushioning. For women, another recommendation is not to wear high heels for too long, as the elevation of the heel alters the position of the arch, overloading it.
Maintaining ideal weight: knowing and keeping your ideal weight is vital, as being overweight can increase the load on the arch and consequently cause pain. One of the calculations to determine whether you are below or above your ideal weight is the Body Mass Index (BMI), developed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Adapting to sports: engage in physical activities, always wear comfortable shoes, and be cautious with excessive wear and tear during training, as the foot muscles may not be prepared for the sudden onset of activity and alternate exercises to avoid overloading a specific structure.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)

How to purchase your custom shoe or insole?
It’s fast and easy! Schedule a free evaluation of your feet with our specialists to buy your custom-made shoe.
Call, send a message to WhatsApp at 4003-8883, or visit: www.pessemdor.com.br/agendamento.
How does the evaluation work?
Upon arriving at a Feet Without Pain branch office, you will be received by a foot, ankle, and knee specialist, who will then fill out a registration form and ask some questions about your pain. Next, the assessment of the feet begins.
The specialist will examine your feet to understand your foot pains and complaints. Then, using the high-precision 3D scanner device, the specialist captures your feet’ measurements.
We are the only company with a 3D scanner for designing custom shoes. First, with the measurements of your feet, a mold is created using 3D printers, and after that, we start making your shoe.
How long does it take for the shoes and insoles to be ready?
Feet Without Pain produces custom-made shoes in up to 3 days; then, they are sent to your home free of charge!
Is the evaluation free?
Our assessment is completely free! We perform a complete analysis of your feet and legs, and you pay nothing for it!
Do we accept medical insurance?
We do not work with insurance because our assessment is completely free! But you can check if your plan somehow refunds you regarding the shoes!
EXTERNAL LINKS
1) Biomechanics of the Foot | NCBI
3) Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction | Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research