Midfoot
The foot can be divided into three regions, the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot. Midfoot pain, as the name implies, is felt in the middle of the foot, between the heel and metatarsal region. Its scientific name is rarely used, and even though the area is structured by bones, joints, and tissues with complicated nomenclatures, it is vital to know a little about each part. Only then a broader notion of the injuries that affect it is possible.
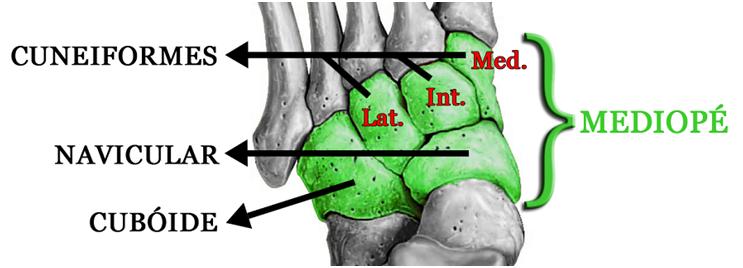
The midfoot comprises five distinct bones: the navicular, the cuboid, and the medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiforms. This region is separated from the forefoot and hindfoot by two specific joint lines: the Chopart joint, which subdivides the foot into the hindfoot and midfoot, and the Lisfranc joint. It is formed by the articulations between the talus and the navicular and between the calcaneus and the cuboid. The Lisfranc joint subdivides the foot into midfoot and forefoot. It is formed by the joints between the three cuneiforms, the first three metatarsals (1st, 2nd, and 3rd), the cuboid, and the two lateral metatarsals (4th and 5th).
To better identify pain, we can divide the midfoot into two regions, the dorsum (top part) and the sole (bottom part). In addition to the bones, the plantar fascia is another component greatly affected in the midfoot. The bones form the longitudinal arch of the foot, a region of great mobility responsible for cushioning the step and adapting the foot to the ground. Conversely, the fascia is a fibrous tissue extending from the calcaneus to the metatarsal bones, maintaining the arch structure and cushioning impacts.
In general, the back region of the foot is more resistant, as it receives the initial load during the step, as this will arrive concentrated and with greater pressure. The front region of the feet, the forefoot, is more mobile and has longer bones and musculature, which will help with propulsion. Therefore, the midfoot performs the function of cushioning and transferring weight from one region to another.
CAUSES
Several factors can cause pain in this region of the foot. As it performs a critical function and is highly required, any change in its structure or overloading of the area may affect it and cause discomfort. The most common pathologies that generate pain in this region are:
Plantar Fasciitis
Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of pain in the midfoot region. It is a plantar fascia inflammation, a fibrous tissue located at the bottom of the foot from the heel to the base of the fingers. It occurs due to intense regional stress, such as repetitive impact or excessive load. In addition, it may present as a symptom: pain in the heel or arch of the foot, which usually happens early in the morning or after more rigorous exercise.
Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency (collapsed arch)
The posterior tibial tendon passes on the ankle inside and inserts into the midfoot bones and the 2nd to 4th metatarsals. Therefore, moving the site and supporting the foot arch is vital. When the tendon is overloaded and inflamed, pain in the plantar region and difficulty standing on tiptoe may sometimes be felt. In addition, according to the study “Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction”, the lesion can increase, generating tissue micro-fissures and loss of function, which causes the gradual lowering of the foot’s arch.
Cuboid syndrome
Cuboid syndrome is a minor disorder or displacement of the cuboid bone located in the outer lateral region of the midfoot. The dislocation can irritate the joint capsule, the ligaments, and the long fibular tendon, leading to considerable pain in the area. The syndrome is rare and usually results from a twisting of the torso for the outside. The reports of cases are more frequent in dancers and athletes due to repetitive effort and area overload.
Navicular syndrome
The navicular bone, located in the inner lateral region of the foot, is rigidly stabilized by an extensive network of ligaments. Due to the squared position of the bone and two strong ligaments, fractures are much more common than their displacement.
Traumatic fractures
Fractures in this region are less frequent, especially in children, due to their joint mobility. Those involving the midfoot are usually caused by direct trauma (such as a heavy object falling) or indirect trauma (sprains and vehicle accidents, for example). That’s why men are more affected by the injury, especially those who practice sports, since they are prone to shocks, traumas, and blows. This fracture is usually extensive and attacks the ligaments and tendons. The symptoms are intense pain, swelling in the region, bruising, and difficulty supporting the foot on the ground. Below are the most common traumatic fractures:
Lisfranc fracture
A Lisfranc fracture is a traumatic bone injury to the joint line that connects the midfoot to the forefoot region (the metatarsals). Because it is very complex, it can only be identified by radiography. However, as there are few cases, the initial evaluation usually does not notice it.
Navicular Fracture
The navicular bone is located in the highest portion of the plantar arch. Much of its bone surface is covered by cartilage, which leads to limited circulation, worsening the prognosis of tissue recovery. They are classified into 3 types of fractures:
– Cortical avulsion fracture: these are usually minor fractures caused by traction on a ligament that pulls out a small bone fragment;
– Fracture of the medial tuberosity: fracture caused by traction of the tendon and ligament inserted into the bone. It usually happens when there is an ankle sprain – a situation where the foot turns out;
– Fracture of the navicular body: severe fractures caused by intense trauma, such as significant falls or motorcycle accidents. Bone fragmentation usually occurs in several small parts of the midfoot.
RISK FACTORS
Arch height
The arches of the foot are formed by bones and the plantar fascia. They are essential to distribute the weight deposited on the feet, avoiding pressure accumulation in specific regions. People with flat feet and pes cavus are more likely to feel pain in the midfoot because when there is an anatomical variation in arch height, there is also a loss of cushioning efficiency and impact absorption in the feet.
Foot types
There are three types of feet: neutral, cavus, and flat. See below the characteristics of each of them:
– The neutral foot has a well-distributed and balanced arch. It is the most suitable for receiving the load and cushioning the impact;
– The pes cavus has a higher and more protruding arch. The support region in this type of foot is reduced. Poorly positioned bones can increase joint friction and strain ligaments. In addition, the plantar fascia is strained, a factor that contributes to its inflammation. The bones that form the arch become compressed;
– Flat foot is made up of a lower arch. In it, practically the entire sole touches the ground, so we consider that this type has a broad support area. However, the plantar fascia in flat feet is stretched and overloaded, decreasing its cushioning capacity.
Types of footstep
Like the foot, the step is classified into three types: pronated, supinated, and neutral. They are characterized according to the foot and ankle movement during the step, mainly due to possible biomechanical misalignments.
– In the pronated footstep, the ankle makes an inward movement, which changes the alignment of the foot joints while walking. This causes poor cushioning and load distribution, concentrated in the inner region of the sole;
– In the supinated footstep, the movement of the ankle during the step is towards the outside. Likewise, it misaligns the joints, worsening cushioning, and weight distribution, concentrated on the outside of the sole;
– The neutral footstep is the most balanced. Support starts mid-heel, and pressures are more evenly distributed across the foot. The ankle and midfoot are aligned.
Specialists recommend a test called baropodometry, performed while standing or walking to find out what type of footsteps you have. As pain is usually aggravated by movement, dynamic baropodometry is the best to identify pressure distribution during walking.
Overload
Because they are the support base of the body, the feet are under constant pressure. However, if the limit is exceeded, the structures that form them will be overloaded and may suffer injuries. The most common ways that lead to overload are weight gain, intense training with little interval, and inadequate movements.
Trauma
They are more common in athletes and motorcyclists since they are more exposed to accidents with foot impact. They are also frequent in the elderly and women in menopause because the bone is fragile and more prone to fractures in these cases. The main consequence of these types of trauma is the modification of anatomy and tissue composition, impairing biomechanics.

PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
An accurate diagnosis is always necessary for effective treatment. Therefore, it is essential to be assessed by a specialist, who, just by palpating two feet and asking a few questions, will be able to identify the problem in some cases. In others, complementary imaging tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Prevention is as crucial as treatment. For this, one must respect the limits of one’s body in training and other physical activities. Two mandatory tips are protection (avoiding trauma and new injuries) and rest (reducing activities that cause pain). In addition, we can take some basic precautions to stay safe, or during the injury treatment. They are the following:
Weight
It is crucial to maintain the ideal weight. Obesity is a disease that, in addition to causing damage to the cardiovascular system and other parts of the body, also affects the feet. Being overweight increases the load on the feet and can cause foot pain.
Equipment
The use of safety equipment is mandatory in several professions and, mainly in traffic. High-impact sports usually have protective equipment to ensure the physical integrity of their practitioners. Always use the appropriate protective gear for activities with a higher risk of trauma to prevent injuries.
Physiotherapy
Look for a specialized physiotherapist for help in containing the inflammatory process. Several therapeutic resources can be used, such as manual therapy, strengthening, electrotherapy, kinesiotherapy, bandage, and needling. Physiotherapy assists in reducing pain, improves joint stability, and helps gain strength.
Orthoses
In less severe cases, using orthoses for treatment is very common. Night splints help maintain correct foot positioning during the night, preventing fascia contraction. The cane, used on the opposite side of the affected foot, helps to reduce the load on the affected foot while walking. In addition, the insoles help improve foot cushioning and foot alignment.
Surgery
Surgeries are recommended only in serious situations where some tissue ruptures. Especially in traumatic injuries, where bone fragmentation and damage to the surrounding tissues occur, surgery may be necessary for structural repair.
FOOTWEAR
Footwear is one of the factors that most influence foot pain. However, knowing how to choose them is a complicated task. They can even damage the area if aesthetics weigh more than comfort at purchase. We can prevent midfoot pain by avoiding dress shoes with narrow points, high heels, or with very rigid and thin soles. They compress the feet and change the adequate structural alignment, compromising their functioning.
Wearing shoes suitable for the activity is recommended to protect your feet. They should be comfortable and have a length gap of about 1.5 cm to prevent them from being squeezed during day-to-day activities and exposed to injury.
CUSTOM SHOES AND INSOLES FEET WITHOUT PAIN® FOR MIDFOOT PAIN
Feet Without Pain custom insoles and shoes are an excellent way to solve midfoot pain and avoid it in other regions. The insole will accommodate all the curves of the sole of your foot, guaranteeing pressure redistribution and avoiding overload. On the other hand, custom-made shoes will consider your feet’s measurements, such as length, width, and circumference, avoiding friction or pressure points and ensuring absolute comfort.

For insoles and shoe manufacturing, it is necessary to be assessed by one of our foot specialists to identify the reason for the pain. Examinations include baropodometry to see the pressures and gait alignment and 3D scanners to know the foot arch shape and position. Other benefits of using Feet Without Pain custom-made insoles and shoes are shown below:

Feet Without Pain Custom Unisex Shoes | There are more than 20 female and male models to choose from.
- Elimination or reduction of pain;
- Injury prevention;
- Increased comfort;
- Perfect fit;
- More time standing without pain;
- Prevention of pathology progression;
- Improved impact cushioning;
- Improved sports performance.
SPORTS
Midfoot pain is widespread in athletes due to the wear and tear of the fascia and instep along with the area’s bones and joints. Any activity demands a lot of effort from the midfoot, so taking care of the place is extremely necessary. For example, the area can hurt in football because of the kick with the “instep”. Likewise, fights like Muay Thai and Kung Fu can wear the same region because of the activity’s impactful kicks and repetition. Besides, running, basketball, and volleyball can also cause midfoot pain, mainly due to the intense contact of the foot with the ground.
Most sports present circumstances that can cause pain in the region since the midfoot is very wide and performs several functions. Therefore, it is essential to avoid training overload by wearing good quality sneakers for exercising and not forgetting impact-absorbing insoles. Many athletes believe pain is part of healthy physical effort and continue to practice, even feeling it. This behavior can potentialize injuries in the midfoot and other structures.
If the pain already exists, the recommendation is to seek an expert to assess it carefully. Only then can the treatment be efficient and complete, facilitating the athletes’ return to their activities. It is known that high-impact sports increase the likelihood of injury and joint wear. However, it is crucial to think more about the movement execution than about the load itself. By carefully guided sports practice, with progressive training and movement correction, the chances of injury can be reduced, decreasing the risk of arthrosis.
TIPS AND CURIOSITIES
Putting ice: it helps to reduce discomfort quickly and accurately. You should apply it between 15 and 20 minutes. Due to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, specialists recommended using ice during periods of pain and right after exercising or returning from work to control possible inflammations;
Anti-inflammatory: Pain medication must be only used under medical advice. They are suitable for containing the inflammatory process and pain, but when misused, they can lead to unwanted effects;
Massage: massage helps to increase local blood circulation and relax the musculature of the region. If the reason for the pain is excessive tensioning of the fascia, massage by hand or with a tennis ball can help;
Rest: Decreasing the load on the injured foot is essential. Specialists recommend walking less during recovery so the foot’s wounded tissues can heal properly.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)

How to purchase your custom shoe or insole?
It’s fast and easy! Schedule a free evaluation of your feet with our specialists to buy your custom-made shoe.
Call, send a message to WhatsApp at 4003-8883, or visit: www.pessemdor.com.br/agendamento.
How does the evaluation work?
Upon arriving at a Feet Without Pain branch office, you will be received by a foot, ankle, and knee specialist, who will then fill out a registration form and ask some questions about your pain. Next, the assessment of the feet begins.
The specialist will examine your feet to understand your foot pains and complaints. Then, using the high-precision 3D scanner device, the specialist captures your feet’ measurements.
We are the only company with a 3D scanner for designing custom shoes. First, with the measurements of your feet, a mold is created using 3D printers, and after that, we start making your shoe.
How long does it take for the shoes and insoles to be ready?
Feet Without Pain produces custom-made shoes in up to 3 days; then, they are sent to your home free of charge!
Is the evaluation free?
Our assessment is completely free! We perform a complete analysis of your feet and legs, and you pay nothing for it!
Do we accept medical insurance?
We do not work with insurance because our assessment is completely free! But you can check if your plan somehow refunds you regarding the shoes!
EXTERNAL LINKS
1) Sobre as doenças: Fasciíte Plantar | Reumato USP;
3) Treatment of Cuboid Syndrome Secondary to Lateral Ankle Sprains: A Case Series | PDF.




